
It is essentially a cavity bordered by the temporal bone, sphenoid bone and sella turcica, which contains the pituitary gland. The cavernous sinus is one of the dural venous sinuses within the head. Commonly due to a posterior community artery aneurysm. These aneurysms are thought to have an imminent risk of rupture. The major concern of a new-onset third nerve palsy is a rapidly enlarging cerebral aneurysm leading to compression. diabetes mellitus, giant cell arteritis): thought to be a microvascular event. meningeal metastasis, also known as meningeal carcinomatosis) A variety of conditions can cause a third nerve palsy in this location: Subarachnoid spaceĭamage to the oculomotor nerve in the subarachnoid space typically causes an isolated third nerve palsy (absence of other neurological features). For example, Weber’s syndrome is characterised by ipsilateral third nerve palsy and contralateral hemiparesis. Midbrain lesions are usually associated with other neurological feature and may be part of a wider ‘brainstem syndrome’. It is at risk of damage from a tumour, haemorrhage or ischaemia (i.e.
The oculomotor nucleus is situated in the brainstem. Each location has several possible causes and associated clinical manifestations. These are generally divided according to location.

Transmitted via optic nerve: Retinal fibres transmit this signal via the optic nerve.Light source: Light is shone onto the retina and detected by photoreceptors.This occurs by contraction of circular fibres of the iris (i.e. The basic principle of the parasympathetic pathway is that as light is shone onto one eye there is corresponding equal and symmetrical pupillary constriction. It is mediated by the parasympathetic nervous system and involves the optic and oculomotor cranial nerves.

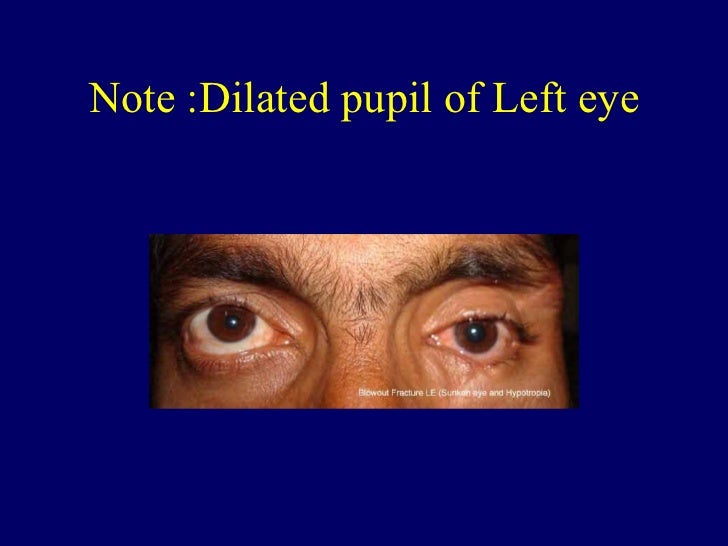
The pupillary light reflex controls the diameter of the pupil in response to light. The third nerve has an important role in the pupillary light reflex. Extraocular muscles: innervates all the extraocular muscles except the superior oblique and lateral rectus muscle.Eyelid: innervates the levator palpebrae superioris that elevates the eyelid.Pupil: parasympathetic fibres run superficially within the nerve to cause pupil constriction.The third cranial nerve has a small number of sensory fibres, but is predominantly a motor nerve that innervates ocular structures. Inferior branch: Innervates medial and inferior rectus muscles, inferior oblique, and pupillary sphincter.Superior branch: innervates levator palpebrae and superior rectus.

It then enters the superior orbital fissure and divides into superior and inferior branches. The third nerve nucleus is comprised of several subnuclei that innervate important visual structures.įibres from these nuclei pass from the midbrain into the subarachnoid space and then into the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus. The third nerve nucleus originates in the midbrain of the brainstem.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
